Fraser Photinia for Sale
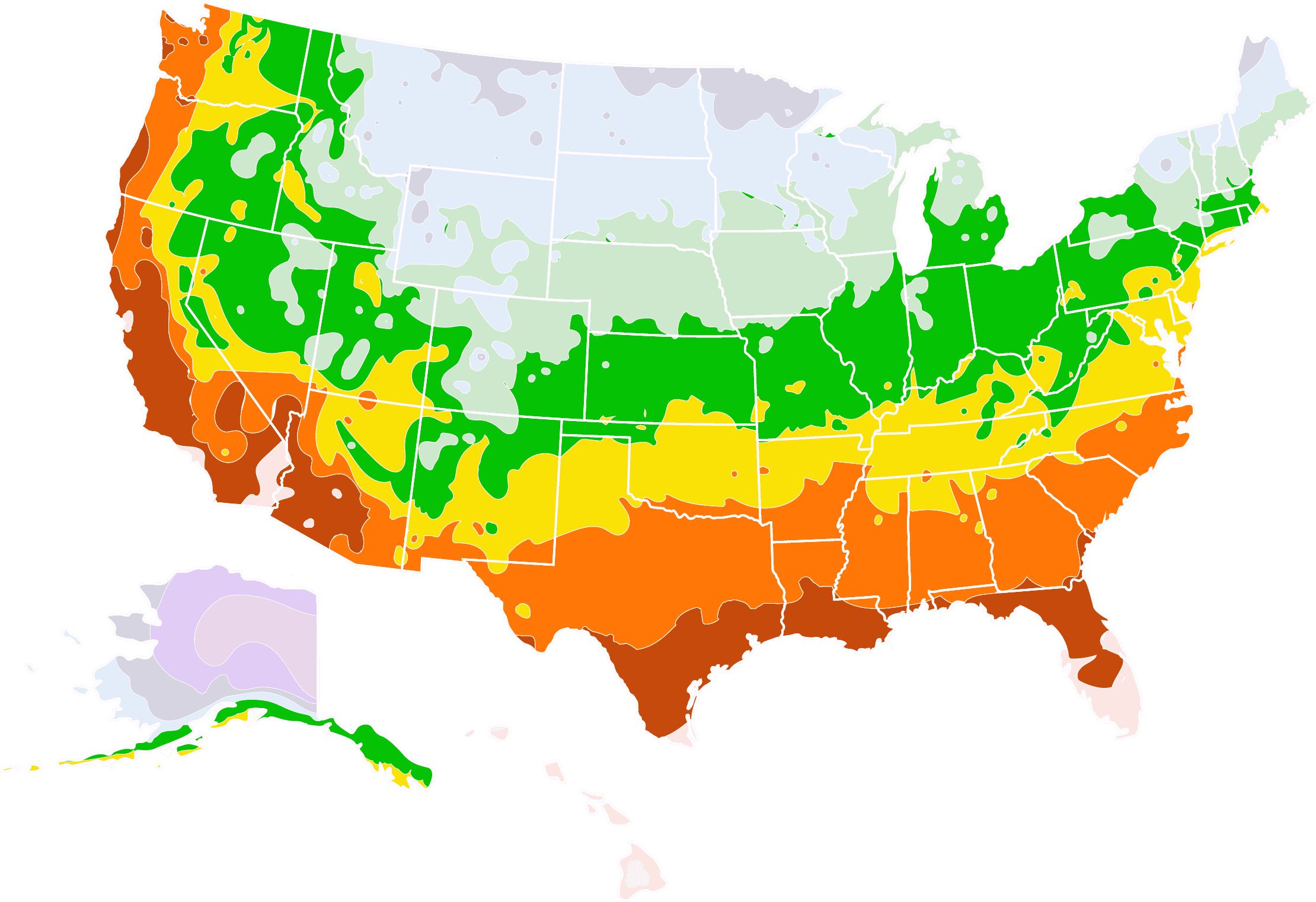
Red tip photinia is an evergreen shrub whose name indicates its most striking feature of vivid, red leaves that occur on new growth in spring and summer. Photinia x fraseri is a hybrid and is used frequently for privacy screens and hedges in the southern U.S. It is best grown in USDA hardiness zones 7-9. Red tip photinia grows quickly and is tolerant of poor soil. It is often grown near roads because it's not overly bothered by road salting in the winter. One of the few drawbacks to photinia is the small white flowers, which have an unpleasant, fetid odor.
- New growth in spring features bright red leaves.
- Makes an excellent hedge.
- Flowers have an unpleasant smell.
Enter your zip code to find nearby stores that may carry this plant.
Plant Care
Sunlight

Partial to full sun daily and grows best with at least four hours of sun a day.
Watering
Can handle short periods of drought once established but thrives on water weekly when young.
Fertilizing

Avoid over-fertilizing. Give it a light dressing of balanced slow-release fertilizer in the spring.
Planting and Care
Planting instructions
Choose a site for your photinia that gets at least partial sun, four hours or more is best, and dig a hole that’s twice as wide and deep as the plant’s root ball. Backfill the hole with some of the soil mixed with compost or well-rotted manure, and place the plant so that the top of the root ball is level with the ground. Continue filling in the soil around the root ball, tamping down to eliminate air pockets. When the hole is filled, water well and add an organic mulch around the root zone.
Watering and nutrients
Water regularly during the first year. Avoid wetting the leaves by directing your hose at the base of the plant, or use a soaker hose. This prevents the growth of fungi that can damage your plant. After the plant is established, it should not need supplemental watering, except in lengthy periods of drought.
For the first year or two, give your photinia a spring feeding with a balanced, 10-10-10 slow-release fertilizer. Once the plant is well established, you do not need to feed it unless your soil is of poor quality.
Pruning
Red tip photinia has a nice spherical shape but you may want to do some light pruning to form your bushes into a hedge. Late winter is the best time for this. Check regularly for broken or diseased branches and remove them when you find them. Light pruning will also encourage new red-leafed growth.
Pests, diseases, and animals
Photinia is prone to fungal diseases, which can spread quickly in a hedge if one plant succumbs to them. Careful watering that avoids wetting the leaves can help minimize the risk. Photinia may also suffer from fire blight, leaf spot, or powdery mildew.
Insect pests that may bother your photinia include several species of mites, the European fruit-tip moth, and scale insects. They may be controlled by encouraging or releasing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, or by using neem oil.
Most animals will not bother a photinia, although birds enjoy eating the plant’s small red berries.
Achieving maximum results
Red tip photinia is best used in one of two ways, as an informal or formal hedge near a road or driveway, that can take advantage of the plant’s tolerance for road salt and other impurities, or as an ornamental, multi-stemmed tree, that is pruned into an upright and attractive shape. You may want to avoid placing it near an area where people gather, such as a picnic table or barbecue pit. This might cause problems when the plant is in bloom, as the smell of the flowers is likely to discourage people from standing close to it.
FAQs
Is red tip photinia a good pollinator?
Yes, it is a good pollinator. Those evil-smelling flowers attract bees, birds, and other pollinators making the plant a good companion for fruit trees and other ornamental plants where pollination is desired.
Is red tip photinia poisonous?
Photinia’s berries should not be eaten by humans or household pets, although they are harmless to birds. They should also never be planted where livestock, such as cattle, graze as the leaves and berries are toxic to them.
What are some of the best varieties of red tip photinia?
Photinia x fraseri ‘Red Robin’ is one popular variety commonly found in garden centers. It grows up to 12 feet high and makes an effective hedge. A similar variety is ‘Little Red Robin,’ which only grows to three feet. Photinia x fraseri ‘Pink Marble’ is a newer variety with particularly beautiful, pinkish-red leaves./p>
What’s the best way to handle fungal outbreaks on my photinia?
Your photinia is susceptible to fungal diseases such as leaf spot and powdery mildew during wet weather. Allow space between your photinia plants and don’t plant them too close to buildings or other structures. Once infected, prune out diseased branches, to prevent spreading. Spray with a fungicide regularly, if you live in a rainy area.
How do I propagate red tip photinia?
As a hybrid, the best way to increase your photinia plants is by stem cuttings. Clip off a branch that has at least three or four leaf nodes, and comes from a part of the plant where the branches are semi-woody, rather than from new growth. Dip the end of the branch in rooting hormone and place it in a pot filled with a mix of vermiculite and perlite. Keep the mix damp, and leave the pot in a protected area with indirect sunlight. Roots should appear from one to five months after.